NOrB3RTO
By Miguel | About Norb3rto.art | Work
More Writings @ ✍️ Writers.Work
Sci-Fi Writings | Poetry | Art
I AM NORB3RTO ✍️
Creating a space is where storytelling meets visual creativity, blending my love for art, photography, and science fiction.
Quantum Shadows
In 2145, Earth thrived on the technological marvel of the Quantum Nexus, a device that allowed exploration of alternate dimensions.
Robotics and Cybersecurity
It highlights the importance of incorporating robust security measures in robotic systems, discusses potential vulnerabilities, and provides recommendations for safeguarding against cyber threats.
A Penetration Testing Toolkit
This technical document aims to provide an overview of various tools that hackers can use to enhance their penetration testing toolkit.
Cybersecurity and Drones
With this rise in drone usage comes a new set of security challenges that must be addressed.
Space Cybersecurity
As we venture further into the depths of outer space, exploring new frontiers and establishing a presence beyond Earth, the need to protect our space assets from cyber threats becomes increasingly paramount.
Emerging Tech in Cybersecurity
Let's delve into cutting-edge technologies that offer innovative solutions for detecting, preventing, and mitigating cyber threats.
Ransomware Attack: Mitigation
A ransomware attack is a malicious cyber threat that can wreak havoc on individuals and organizations. It involves cybercriminals' unauthorized encryption of files or systems, who then demand a ransom to restore access to the compromised data.
Hacking in Self-Driving Cars
Hacking into self-driving cars has become a prominent concern due to the increasing popularity of autonomous vehicles. As technology advances, hackers are presented with new opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities within these vehicles.
Cybersecurity for EV Charging
EVs' growing popularity and adoption necessitate addressing the potential vulnerabilities and threats associated with EV charging infrastructure.
DeFi Security: Addressing Risks
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has revolutionized traditional finance by eliminating intermediaries and offering users unprecedented access to various financial services.
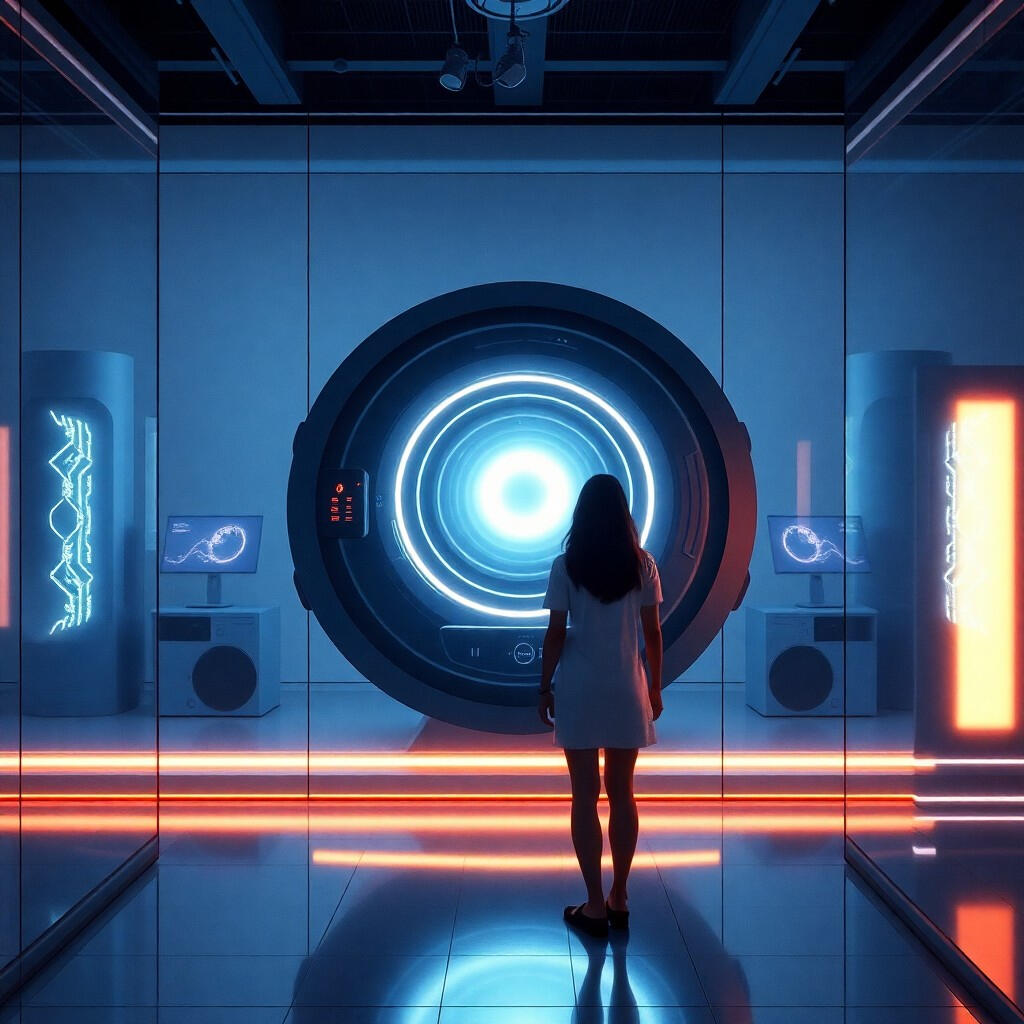
Quantum Shadows
In 2145, Earth thrived on the technological marvel of the Quantum Nexus, a device that allowed exploration of alternate dimensions.Marin Wells, a quantum engineer, was celebrated for her expertise with the Nexus, yet she was haunted by a recurring anomaly—a shadow that flickered at the edge of her consciousness during experiments.Intrigued, Marin theorized this shadow was a remnant of her consciousness from a parallel universe. Driven by curiosity, she devised an experiment to confront it. Activating the Nexus, Marin was pulled into a mirrored version of her lab. There, she met another Marin, identical in appearance but carrying the weight of different choices.The two locked eyes, sharing an unspoken understanding of their intertwined existences. The mirrored Marin reached for the Nexus console, causing reality to fracture. Marin found herself back in her own lab, alone and disoriented. The shadow was gone, leaving behind a whisper of its presence.Strangely, her reflection in the glass wall began to move independently, smiling when she did not, with eyes glowing with otherworldly light. Marin realized the experiment had fractured reality, merging her consciousness with countless alternate selves.Her journey through the Quantum Nexus had only just begun, as she pondered her next move, knowing she was no longer alone within her own mind.
AI in Cybersecurity
One critical area where AI is playing a crucial role is cybersecurity. This document highlights how AI can help enhance cybersecurity measures and mitigate the growing cyberattack threats.Utilizing AI for Threat DetectionAI algorithms analyze vast amounts of data with incredible speed, making them well-suited for detecting patterns and anomalies in network traffic, user behavior, and system logs. By leveraging machine learning techniques, AI systems can learn from historical data to identify potential threats that may have gone unnoticed by traditional security systems.Intrusion Detection Systems (IDS)AI-powered Intrusion Detection Systems continuously monitor network traffic for suspicious activities. These systems employ machine learning algorithms to detect known attack patterns and identify previously unknown threats based on abnormal behaviors. This enables organizations to respond promptly to potential attacks before they can cause substantial damage.User Behavior Analytics (UBA)Organizations can detect compromised user accounts or insider threats by employing AI-based User Behavior Analytics. Machine learning models analyze users’ behavior patterns, such as login times, access privileges, and activity logs, to identify deviations or unauthorized actions that may indicate a security breach.AI-Powered Threat PreventionIn addition to threat detection, AI can contribute significantly to preventing cyberattacks by proactively identifying vulnerabilities and securing systems against threats.Vulnerability AssessmentAI algorithms can automatically scan software codebases or system configurations to pinpoint potential vulnerabilities. By analyzing millions of lines of code or system settings within seconds, these tools assist developers and system administrators identify weak points that attackers could exploit.Adaptive AuthenticationTraditional authentication methods like passwords are becoming less secure due to increasing credential theft. AI provides adaptive authentication solutions that leverage multiple factors, such as device recognition, biometrics, and behavior analysis, to verify user identities accurately. This enhances security by reducing the risk of unauthorized access through stolen or compromised credentials.AI-Powered Incident ResponseAI can help organizations respond effectively and efficiently when a cybersecurity incident occurs by automating various aspects of the incident response process.Automated Threat HuntingAI-powered threat-hunting tools scan networks and systems in real-time, leveraging machine learning algorithms to identify indicators of compromise (IOC) and potential threats. Organizations can significantly reduce response times and quickly contain incidents before they escalate by automating this process.Chatbot-Based Incident TriageAI-powered chatbots can assist security analysts in triaging incidents by immediately responding to inquiries and suggesting initial remediation steps. These chatbots can utilize natural language processing algorithms to understand users’ queries accurately, helping them navigate complex incident response procedures more efficiently.Last ThoughtArtificial Intelligence has emerged as a powerful ally in the fight against cyber threats. AI is transforming the cybersecurity landscape with its ability to analyze vast amounts of data, detect anomalies, prevent attacks, and facilitate incident response processes. Embracing AI technologies empowers organizations to strengthen their defenses against evolving cyber threats and safeguard sensitive information effectively.
Robotics and Cybersecurity
This technical document explores the intersection of robotics and cybersecurity. It highlights the importance of incorporating robust security measures in robotic systems, discusses potential vulnerabilities, and provides recommendations for safeguarding against cyber threats.RoboticsRobotics involves designing, developing, and operating robots that can perform tasks autonomously or with human assistance. These robots can have various applications in manufacturing, healthcare, agriculture, and other industries.Cybersecurity in RoboticsAs robotics increasingly integrates into various domains, ensuring their security is paramount. The interconnectedness and reliance on network infrastructure expose robotic systems to potential cyber threats that could compromise their functionality or even cause harm.Potential Vulnerabilities in Robotic SystemsRobotic systems can be vulnerable to a range of cyber attacks due to several factors:a) Inadequate Authentication MechanismsWeak authentication methods can allow unauthorized access to robotic systems, potentially leading to unauthorized control or manipulation.b) Insufficient Encryption PracticesInadequate encryption techniques may expose sensitive data transmitted between the robot and external systems, making it susceptible to eavesdropping or data tampering.c) Lack of Secure Communication ProtocolsThe absence of secure communication protocols can enable attackers to intercept or manipulate data exchanged between robots and other connected devices.d) Remote Code Execution VulnerabilitiesRobotic systems that rely on software components might be prone to vulnerabilities that allow remote code execution by malicious actors.e) Physical Security RisksPhysical access to robotic systems could result in unauthorized modifications or tampering, compromising their integrity and functionality.Recommendations for Enhancing Robotic CybersecurityTo mitigate potential cybersecurity risks associated with robotics, consider implementing the following measures:a) Strong Authentication MechanismsEmploy robust authentication methods like multifactor authentication (MFA) to ensure that only authorized individuals can access and control robotic systems.b) Secure Data EncryptionImplement robust encryption techniques to protect sensitive data transmitted between robots and external systems, preventing unauthorized access or tampering.c) Use Secure Communication ProtocolsAdopt secure communication protocols (e.g., Transport Layer Security - TLS) to ensure the integrity and confidentiality of data exchanged between robotic devices and other networked components.d) Regular Software UpdatesStay up-to-date with software updates manufacturers provide to address any known vulnerabilities and ensure the latest security patches are applied.e) Physical Access ControlsImplement physical security measures such as restricted access areas, surveillance cameras, and tamper-evident seals to prevent unauthorized physical access to robotics systems.Last ThoughtAs robotics continues to evolve and expand its presence in various industries, addressing cybersecurity concerns becomes increasingly crucial. By implementing robust security measures such as strong authentication, secure communication protocols, and regular software updates, organizations can enhance the resilience of their robotic systems against potential cyber threats.
A Penetration Testing Toolkit
This technical document aims to provide an overview of various tools that hackers can use to enhance their penetration testing toolkit. These tools are designed to assist in identifying vulnerabilities and weaknesses in computer systems, networks, and applications.1. NmapNmap is a powerful scanning tool for discovering network hosts and services. It provides various scanning techniques, including TCP connect, SYN, and UDP scans. Nmap also offers advanced features such as OS detection, version detection, and scripting capabilities.2. Metasploit FrameworkThe Metasploit Framework is a comprehensive open-source penetration testing platform that allows hackers to exploit system vulnerabilities. It provides vast exploits, payloads, auxiliary modules, and post-exploitation tools. The framework supports manual and automated exploitation with its built-in scripting language.3. Burp SuiteBurp Suite is an integrated platform for performing web application security testing. It includes various tools such as a proxy server, vulnerability scanner, and intruder module. Burp Suite allows hackers to intercept and modify HTTP/S traffic between the browser and the target application to identify potential vulnerabilities.4. WiresharkWireshark is a widely-used network protocol analyzer that captures real-time network packets. It enables hackers to inspect packets at the microscopic level and analyze protocols across different OSI model layers. With its extensive filtering capabilities and support for numerous protocols, Wireshark is an essential tool for analyzing network traffic during penetration testing.5. John the RipperHackers use John the Ripper as a popular password-cracking tool for offline password attacks. It supports various encryption algorithms and hash types, allowing the hacker to crack passwords from hashed password databases or stolen password files.6. HydraHydra is a versatile online password-cracking tool that can perform brute-force and dictionary attacks against various network services such as HTTP, FTP, SSH, Telnet, and more. It allows hackers to automate guessing usernames and passwords to gain unauthorized access.7. Aircrack-ngAircrack-ng is a set of tools used for auditing wireless networks’ security. It includes tools for capturing packets, performing cryptographic attacks on WEP and WPA/WPA2-PSK keys, and conducting active de-authentication attacks. Aircrack-ng is invaluable for testing the security of wireless networks during penetration testing.Last ThoughtBy incorporating these tools into their penetration testing toolkit, hackers can enhance their ability to identify vulnerabilities in computer systems, networks, and applications. However, it’s important to note that these tools should only be used for ethical purposes under proper authorization to ensure the security of systems and respect privacy rights.
Cybersecurity and Drones
With this rise in drone usage comes a new set of security challenges that must be addressed. This technical document aims to explore the cybersecurity risks associated with drones and propose solutions to mitigate these risks.Cybersecurity Risks2.1 Unauthorized AccessOne of the primary cybersecurity risks in the context of drones is unauthorized access to their control systems or data transmission channels. Hackers may attempt to gain control over drones to carry out malicious activities or steal sensitive information.2.2 Data PrivacyDrones are capable of capturing and transmitting vast amounts of data. This data can include images, videos, location information, and other potentially sensitive data. Protecting this data from unauthorized access is crucial to ensure privacy and prevent misuse.2.3 Manipulation of Flight SystemsCyber attackers may attempt to manipulate a drone’s flight systems by exploiting vulnerabilities in its software or communication protocols. This could result in unauthorized control over the drone’s movement or even cause physical damage.Mitigation StrategiesTo address the cybersecurity challenges related to drones, several mitigation strategies can be implemented:3.1 Secure Communication ChannelsImplementing robust encryption protocols for drone communication channels is essential to protect against eavesdropping and unauthorized access. This ensures that transmitted data remains confidential and integrity is maintained.3.2 Authentication MechanismsImplementing robust authentication mechanisms will help verify the identity of authorized users accessing drone systems or controlling them remotely. This prevents unauthorized individuals from gaining control over drones.3.3 Software Updates and Patch ManagementRegular software updates and patch management are crucial to address vulnerabilities that may be discovered in drone software. Patches should be promptly installed to mitigate the risk of cyberattack exploitation.3.4 Data Encryption and AnonymizationSensitive data captured by drones should be encrypted both during transmission and storage. Additionally, anonymizing data whenever possible can help protect privacy and prevent unauthorized identification of individuals or organizations.3.5 Intrusion Detection SystemsImplementing intrusion detection systems (IDS) can help identify suspicious activities or attempts to compromise drone systems. IDS can monitor network traffic, behavior patterns, and system logs to detect potential cyber threats in real time.As the use of drones continues to expand across industries, it is crucial to address the cybersecurity challenges they bring. By implementing effective mitigation strategies such as secure communication channels, authentication mechanisms, software updates, data encryption, and intrusion detection systems, we can ensure the security and integrity of drone operations. Organizations and individuals must prioritize cybersecurity measures to safeguard against evolving threats in this technological landscape.
Space Cybersecurity
As we venture further into the depths of outer space, exploring new frontiers and establishing a presence beyond Earth, the need to protect our space assets from cyber threats becomes increasingly paramount.Space CybersecurityIn an interconnected world where technology governs almost every aspect of our lives, it is no surprise that space missions heavily rely on sophisticated systems and networks. From satellites providing vital communication links to spacecraft controlling various operations, our reliance on these technologies makes them lucrative targets for malicious actors seeking to exploit vulnerabilities.Secure Communication ChallengesOne of the primary concerns in space cybersecurity is ensuring the integrity and confidentiality of data transmitted between Earth and space. The vast distances involved create unique challenges in maintaining secure communication channels. Encryption protocols must be robust enough to withstand attempts at interception or tampering while accounting for the time delays inherent in long-distance communication.Protecting Physical InfrastructureMoreover, protecting the physical infrastructure of space assets is equally important. Satellites orbiting thousands of kilometers above us are vulnerable to physical attacks by hackers attempting to disable or take control of them. Ensuring proper authentication protocols and implementing stringent access controls are essential to prevent unauthorized manipulation or sabotage.Defense against Internal ThreatsAnother critical aspect of space cybersecurity involves defending against cyber threats from within the confines of a spacecraft. Crewed missions risk onboard systems being compromised by malware or unauthorized access, potentially jeopardizing mission objectives and crew safety. Implementing strict security measures and regularly updating software patches can help mitigate these risks.Autonomous Spacecraft SecurityFurthermore, the ever-expanding field of autonomous spacecraft introduces its cybersecurity challenges. As we develop technologies like autonomous rovers or drones for extraterrestrial exploration, we must carefully consider potential vulnerabilities that hackers could exploit to disrupt scientific endeavors or gain unauthorized access to sensitive information.As humanity ventures deeper into space exploration, safeguarding our space assets from cyber threats becomes imperative. By developing robust cybersecurity measures, such as secure communication protocols, physical infrastructure protection, and defense against internal and external cyber threats, we can ensure our space missions' continued success and safety. With adequate precautions, we can confidently continue our journey beyond Earth's boundaries while safeguarding the invaluable knowledge and discoveries awaiting us in the vastness of space.
Emerging Tech in Cybersecurity
Let's delve into cutting-edge technologies that offer innovative solutions for detecting, preventing, and mitigating cyber threats. By embracing these emerging technologies, we can strengthen our defense mechanisms and safeguard critical systems against malicious actors.Artificial Intelligence (AI) and Machine Learning (ML)AI and ML algorithms have become powerful tools for cybersecurity professionals. They can identify patterns, anomalies, and potential threats by analyzing vast data. AI-powered security systems can detect and respond to attacks in real time, enhancing the overall capabilities of traditional security measures.Blockchain TechnologyBlockchain is not limited to cryptocurrencies; its decentralized nature makes it an ideal solution for enhancing cybersecurity. Its immutable ledger ensures data integrity, making it difficult for hackers to alter or manipulate information. Blockchain technology can be applied to secure transactions, identity management, supply chain security, and more.Internet of Things (IoT) SecurityAs IoT devices proliferate, securing them becomes crucial to prevent potential breaches. Emerging technologies focus on securing endpoints, encrypting communication channels, implementing robust authentication methods, and monitoring device behavior for malicious activities.Cloud SecurityWith the increasing adoption of cloud computing services, cloud security has gained prominence—advanced cryptographic techniques secure data at rest and in transit within cloud environments. Additionally, homomorphic encryption allows computations on encrypted data without exposing the underlying sensitive information.Biometric AuthenticationBiometric authentication methods such as fingerprints, facial recognition, voice recognition, and iris scans provide an added layer of security compared to traditional passwords or PINs. These emerging technologies ensure that only authorized individuals can access sensitive systems or data.Threat Intelligence AnalyticsThreat intelligence analytics combines big data analytics with cybersecurity expertise to proactively identify potential vulnerabilities or threats. By continuously monitoring network traffic patterns and analyzing external threat intelligence feeds, organizations can detect and respond to potential threats before they cause significant harm.Emerging technologies are vital in safeguarding sensitive information and combating cyber threats. From AI-powered security systems to blockchain technology and biometric authentication, these technologies are shaping the future of cybersecurity. Embracing these innovations will allow organizations to stay one step ahead in the ongoing battle against cybercrime.
Ransomware Attack: Mitigation
A ransomware attack is a malicious cyber threat that can wreak havoc on individuals and organizations. It involves cybercriminals' unauthorized encryption of files or systems, who then demand a ransom to restore access to the compromised data.The Process of a Ransomware AttackTo understand how a ransomware attack works, let’s examine its stages:Delivery: Typically, the attack begins with the recipient unknowingly downloading or opening an infected file or clicking on a malicious link. This can happen through various means, such as phishing emails, drive-by downloads, or exploiting vulnerabilities in outdated software.Propagation: Once inside the victim’s system, ransomware spreads throughout the network, encrypting critical files and rendering them inaccessible. Sometimes, it may lock down entire systems or seize control over essential functions.Ransom Demand: With their files held hostage, victims often receive a message from the attackers revealing their ulterior motive: demanding payment in cryptocurrency like Bitcoin within a specified timeframe. This coercive tactic exploits the urgency and fear generated by losing critical data.Payment and Restoration: The cybercriminals behind these attacks meticulously design their ransom demands to maximize profits while maintaining anonymity. They typically provide detailed instructions on making payments and restoring access to files once they receive payment confirmation.Mitigation StrategiesTo protect against ransomware attacks, consider implementing these proactive security measures:Software Updates: Regularly update software and operating systems with patches that address vulnerability issues exploited by attackers.Offline Backups: Back up critical files offline so that victims have copies readily available for restoration without paying ransom in case of an attack.Cautionary Practices: Exercise caution when clicking on suspicious links or downloading attachments from unknown sources to significantly reduce the risk of falling victim to ransomware.Anti-malware Software: Employ robust antivirus and anti-malware software to detect and block ransomware threats.Employee Awareness Training: Educate employees about the risks associated with ransomware attacks, including phishing emails and suspicious links, to create an additional layer of defense against these cyber threats.Ransomware attacks pose significant risks to individuals and organizations globally. Understanding how they operate empowers users to safeguard their digital assets proactively. By staying vigilant and employing robust security practices, we can collectively combat this pervasive threat and mitigate its impact on our digital lives.
Hacking in Self-Driving Cars
Hacking into self-driving cars has become a prominent concern due to the increasing popularity of autonomous vehicles. As technology advances, hackers are presented with new opportunities to exploit vulnerabilities within these vehicles. This document explores how self-driving cars can be hacked and the potential risks associated with these vulnerabilities.Communication Systems VulnerabilitiesOne significant vulnerability lies within the communication systems of self-driving cars. These vehicles heavily rely on wireless networks to exchange critical information with other vehicles and infrastructure. However, this reliance allows hackers to intercept or manipulate the transmitted data. Such actions could result in catastrophic consequences on the road, making it vital to address this vulnerability.Sensors and Perception Systems VulnerabilitiesAnother concern is the sensors and perception systems implemented in self-driving cars. These systems collect real-time data from cameras, lidar, and radar sensors to analyze the surrounding environment and make informed driving decisions. Hackers can exploit vulnerabilities within these sensors or tamper with their output, potentially deceiving the vehicle into misinterpreting its surroundings. This manipulation could lead to accidents or intentional harm.Software Infrastructure VulnerabilitiesSelf-driving cars’ software infrastructure can also be subject to cyber-attacks. Hackers may attempt remote access points or exploit weaknesses within the code itself to breach the vehicle’s software. Once inside, they can manipulate critical functions of the car, gaining control over acceleration, braking, or steering mechanisms. Detecting and addressing these vulnerabilities is crucial for ensuring safe operation.Physical Security ConcernsDespite implementing robust cybersecurity measures in autonomous vehicles’ software and hardware components, physical tampering remains possible. Hackers could gain unauthorized access by altering car components or bypassing security mechanisms like authentication protocols. Manufacturers must focus on physical security and digital safeguards to prevent unauthorized access.Evolving Hacking TechniquesAs technology rapidly evolves, hacking techniques also advance. Both manufacturers and consumers must remain vigilant about these vulnerabilities and regularly update their software with security patches. Rigorous testing and risk assessments should be conducted to identify and mitigate potential weaknesses in self-driving car systems.Last ThoughtWhile self-driving cars have the potential to revolutionize transportation, addressing the associated vulnerabilities is crucial. Understanding the potential risks and taking proactive measures to enhance cybersecurity is essential for ensuring a safer and more secure future for autonomous vehicles on our roads. We can mitigate the risks of hacking into self-driving cars by staying informed, regularly updating software, conducting rigorous testing, and implementing robust security measures.
Cybersecurity for EV Charging
EVs' growing popularity and adoption necessitate addressing the vulnerabilities and threats associated with EV charging infrastructure. This technical document aims to highlight the significance of cybersecurity in the context of EV charging infrastructure and provide recommendations to mitigate risks.Benefits and Challenges of EV Charging InfrastructureTransitioning from traditional fuel-powered vehicles to EVs brings numerous benefits, including reduced carbon emissions and lower operating costs. However, it also introduces new challenges in protecting the charging infrastructure from cyberattacks. With an increasing number of EV charging stations installed worldwide, they have become attractive targets for hackers seeking to exploit vulnerabilities or gain unauthorized access.Concerns and RisksOne primary concern regarding EV charging infrastructure cybersecurity is the potential disruption to setting services. If attackers gain control over a charging station, they could manipulate or sabotage the charging process, leading to inconvenience or safety hazards for EV owners. Additionally, compromised charging stations might serve as entry points for infiltrating other connected systems within the electric grid, posing a significant risk to overall energy security.Mitigating Cybersecurity RisksTo mitigate these risks effectively, robust cybersecurity measures need to be implemented across all levels of EV charging infrastructure:Secure Communication Protocols: Ensuring secure communication protocols between the charging stations and backend systems is essential. Encrypting data transmission can prevent eavesdropping and unauthorized access.Robust Authentication Mechanisms: Implementing strong authentication mechanisms for users accessing the charging services adds a layer of security. Multi-factor authentication can help prevent unauthorized access.Regular Updates and Patching: Regularly updating and patching any vulnerabilities detected in system software is critical for maintaining a secure environment.Continuous Monitoring and Threat Intelligence Gathering: Continuous monitoring helps identify potential cyber threats before they can cause harm. Collecting threat intelligence enables proactive defense against emerging risks.Incident Response Procedures: Establishing efficient incident response procedures minimizes damage in case of a successful breach. Preparedness is critical to reducing the impact of cybersecurity incidents.Public Awareness and Education: Prioritizing public awareness about cybersecurity risks related to EV charging infrastructure is essential. Educating users about best practices, including avoiding untrusted third-party apps or websites when accessing charging services, can help prevent phishing or malware injection attacks.
Last ThoughtAs EVs become more widespread, cybersecurity for EV charging infrastructure must be taken seriously. By implementing comprehensive security measures and fostering collaboration between industry stakeholders, we can ensure electric mobility's safe and uninterrupted development while safeguarding against potential cyber threats.
DeFi Security: Addressing Risks
Decentralized Finance, or DeFi, has revolutionized traditional finance by eliminating intermediaries and offering users unprecedented access to various financial services. However, while this technology brings numerous benefits, it also introduces new challenges that must be carefully considered.Smart Contract VulnerabilitiesOne of the critical risks in the DeFi ecosystem is intelligent contract vulnerabilities. Smart contracts are self-executing agreements that run on blockchain networks and power many DeFi applications. These contracts are designed to execute transactions automatically based on predefined conditions. However, if these contracts contain bugs or vulnerabilities in their code, they can be exploited by malicious actors who can manipulate them for personal gain.Economic ExploitsAnother risk factor is economic exploitation. In some instances, attackers can take advantage of price manipulations or liquidity imbalances within decentralized exchanges or lending platforms to profit at the expense of other users. These economic exploits exploit weaknesses in the design of these systems and require continuous monitoring and proactive measures to mitigate their impact.Oracle AttacksFurthermore, there are concerns regarding Oracle attacks in DeFi systems. Oracles are essential components that provide external data feeds to intelligent contracts so they can make informed decisions. However, if an oracle is compromised or manipulated, it can supply incorrect information to a smart contract, leading to undesirable outcomes such as loss of funds for users.User ErrorMoreover, user error remains a significant vulnerability in DeFi systems. Since most transactions are irreversible once executed on the blockchain, any mistakes made by users could result in permanent loss of assets. Individuals must exercise caution when interacting with these platforms and seek proper education or guidance before engaging in complex financial activities.Addressing Risks and VulnerabilitiesCollaborating between developers and auditors is vital to tackle these risks and vulnerabilities effectively. Strong security practices, including robust auditing processes and rigorous testing methodologies, should be implemented to identify and rectify any flaws in the system before they can be exploited. Additionally, continuous research and development are necessary to stay ahead of emerging threats and ensure the long-term security of DeFi platforms.Last ThoughtWhile DeFi has unlocked immense potential for financial inclusivity and innovation, it is essential to recognize and address the risks and vulnerabilities inherent in this ecosystem. By adopting stringent security measures, fostering stakeholder collaboration, and promoting user education, we can pave the way toward a more secure decentralized financial landscape that benefits all participants.
ab0ut
Blending futuristic tales with anime, humanism, and art influences.
Sci-Fi Stories: Gripping plots and imaginative settings.
Art Creations: Enhancing storytelling with AI art.
Stay updated on releases, and exclusive content.
Join journey through sci-fi, and art!
Text





